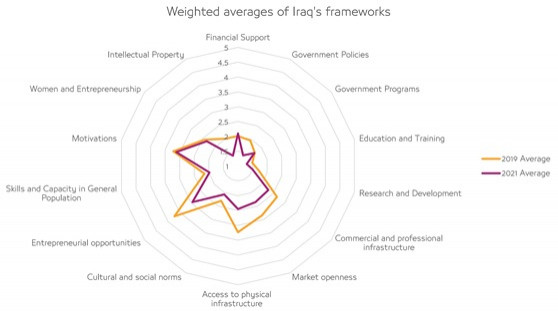
This research explores the influence of the COVID-19 pandemic on the Iraqi entrepreneurial ecosystem and weighs the results against the previous Iraqi Startups Ecosystem Evaluation study published by KAPITA in 2020, to highlight the changes brought about by the onset of the pandemic, and explore comparisons with other selected economies. This publication is part of Business LANDSCAPE series which a series of research publication aims to highlight the current situation of Iraq’s economy and private sector through publishing researches and data and make it freely available for the benefit of investors, and the local and international community This study is published in partnership with German Government via the Deutsche Gesellschaft für Internationale Zusammenarbeit (GIZ) GmbH. |  |
Despite the immense challenge posed by the pandemic, it is in situations such as these that the need to lessen the dependence on the oil industry and shift attention to private sector entrepreneurship is highlighted, as it can help the country become less vulnerable to economic crises, and assist in its recovery. The crisis brings many opportunities along with it and opens the door to new perspectives that enable working and living in different more efficiently. It also displays how innovative and useful entrepreneurship can be in times like this, as it can provide new jobs, incomes, and overall growth to the economy.
• The methodology adopted in this research is based on the Global Entrepreneurship Monitor (GEM) report which has been going for more than 2 decades. The frameworks are constant in their cores throughout the years with some modifications that can be observed in some years.
• Fourteen frameworks are included in the questionnaire with 9 of the frameworks being the core of the questionnaire and on which the experts were selected and country-based comparisons were done.
• A team of experts in entrepreneurship developed a list of experts to be interviewed who are knowledgeable about the nine domains of the questionnaire. These experts could be individuals in governmental institutions, universities, consulting firms, financial agencies, or established entrepreneurs. The experts were not limited to a certain geographic area or a certain industry.
• Convenience sampling was used to identify experts (as adopted by GEM). Thirty experts filled the questionnaire. Years of experience were mainly between 7-12 years with a maximum of 30 years of experience.